Concept of IE:
The garment manufacturing and exporting industry is facing heavy challenges due to various factors including global competition, production costs increase, less productivity/efficiency, labor attrition, etc. the basic fact that our country has immense strength in human resources itself is the motivating aspect to feel for such an analysis. For overcoming those challenges our need industrial engineering knowledge. The formula for Industrial Engineering is might to know every textile student and professionals.
We can see at a glance of IE,
Industrial Engineering (IE) = Production ↑ Cost ↓ Proper use of all elements ↑ Efficiency ↑ Profit ↑
1. Line Labor Productivity: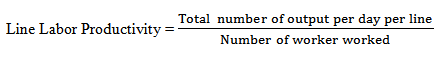
2. Line Machine Productivity:
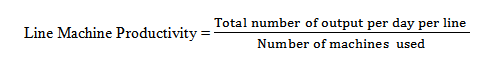
3. Line Efficiency:
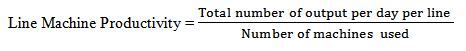
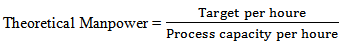
5. Target: 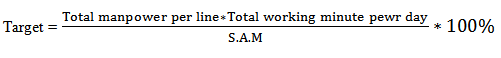
6. Standard Pitch Time: S.P.T = Basic Pitch Time (B.P.T) + Allowances (%)
7. GSD: GSD = (Manpower * Work hour) / Target
8. SMV: SMV = Basic time + (Basic time * Allowance)
9. Basic time: Basic time = Observed time * Rating
10. Observed time: Observed time = Total Cycle time / No of cycle
11. Rating: Rating = (Observed Rating * Standard rating) / Standard rating
12. Earn minute: Earn minute = No of Pc’s (Production) * Garments SMV
13. Available minute: Available minute = Work hour * Manpower
14. Organization Efficiency:
Organization Efficiency = (Basic pis time / Bottleneck time) * 100
15. Basic pis time (BPT): Basic pis time = Total GMT SMV / Total Manpower
16. UCL: UCL = Basic pis time / Organization Efficiency
17. LCL: LCL = 2 * Basic pis time – UCL
18. Capacity: Capacity = 60 / Capacity time in minute
19. Cycle Time: Cycle Time = 60 / Team target
20. Capacity Achievable: Capacity Achievable = Capacity * Balance
21. Daily output: Daily output = Work hour / SMV
22. Factory capacity:
Factory capacity = (Work hour / SMV) * Total worker * Working day * Efficiency
23. CPM:
CPM = (Total overhead cost of the month / No of SMV earners Work minutes) *Efficiency
24. Required no of the operator: Required no of operator = Target daily output / Daily output per operator
25. Efficiency: Efficiency = (Earn minute * Available minute) * 100
Author of this Article:
Md. Zahidul Haque
B.Sc. in Apparel Manufacturing
Senior Executive - IE
A reputed garments Industry in Bangladesh






